Future Now
The IFTF Blog
Investigating future of persuasion with Fogg Behavior Grid
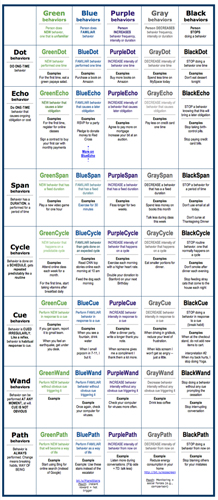
Stanford professor BJ Fogg has recently developed a framework for classifying types of behavior change called, appropriately enough, the Fogg Behavior Grid. The grid is a 7x5 matrix that maps behaviors described by frequency (a one-time behavior, or behaviors over a duration of time, etc) against behaviors described by their direction of change (increasing, decreasing, or cessation) and level of familiarity. This results in 35 fairly specific behavior clusters like BlueSpan behaviors, defined as familiar behaviors that have a fixed duration and exemplified by a behavior to exercise for 30 minutes. Fogg believes that once behaviors can be compared on these dimensions, the same core persuasive strategies to successfully target one behavior should be repurposable to other behaviors in the same cluster.
I'm most intrigued by the Grid as a scaffolding for thinking about future directions in persuasion. Take for example the Cue behavior type, described as a behavior that is cued irregularly and akin to an automatic response—like drinking water when you pass a water fountain or trying to reduce stress levels when you're driving in gridlock. Over the next decade, the situations described in this cluster will increasingly take place in a world of pervasive computing, context-awareness, and geo-coded layers of data. So remembering to grab a drink of water won't be left up to chance, not when you have a powerful mobile device that constantly remembers hydration is a personal goal of yours, compares your location to a geo-coded map of city-wide drinking fountains and sends that info to your augmented-reality glasses displaying the location of the nearest fountain directly in your field of vision.
This post is just a beginning of inquiry but one that I think holds promise, and I'll try to work my way through the Fogg Grid with this future lens and update this post. Forecasting the Future of Persuasion absolutely starts with understanding human behaviors and only then layers future trends and emerging technologies.